A chainsaw carburetor is an essential part that mixes fuel and air in a precise ratio to generate combustion in the chainsaw engine. If this mixture is too rich or lean, the chainsaw may operate poorly, with less power and a greater risk of stalling.
Because of this, it’s essential to have the right proportion of air and fuel in the engine to run efficiently and ensure the chainsaw’s longevity.
Sounds a bit confusing?
Don’t worry, though; by the end of this article, you will have a thorough understanding of;
– how a chainsaw carburetor works.
– which carb parts work together to regulate the fuel and air mixture.
– the process of chainsaw carburetor cleaning and adjustment.
Let’s get started, without any further ado:
Working of a Chainsaw Carburetor: How Does It Operate?
A chainsaw’s carburetor works by combining air and fuel to generate the right fuel mixture for the engine. It has a fuel pipe attached to one side of a vertical air pipe. The middle of the pipe has a narrow kink called a venturi, through which the air passes as it moves through the pipe. As a result, the air pressure decreases, which induces a suction effect that draws fuel from the side pipe. The throttle and the choke are two valves on the carburetor that regulate how much fuel and air enter the engine. You can adjust the choke and throttle valves on the chainsaw carburetor to ensure that the engine gets the correct fuel mixture. This, in turn, results in efficient and reliable operation.
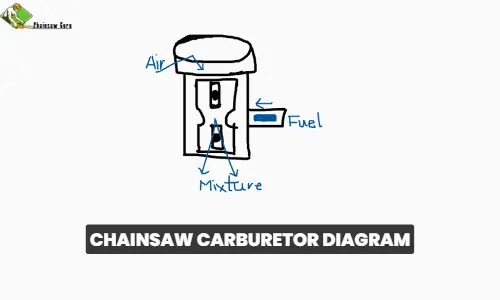
Components of a Chainsaw Carburetor: Exploring the Parts
Throttle Valve
In essence, the throttle in the venturi is a butterfly valve. The throttle valve controls the air and fuel flow when the engine is running normally. At idle, the throttle plate restricts airflow, creating a vacuum on the other side that pulls fuel through the idle jet, a tiny hole in the tube. The carburetor performs optimally at full throttle, allowing air to flow through the tube and creating a vacuum that pulls fuel through the jet.
Choke Valve
At the venturi’s entry is the choke valve, which resembles the throttle. The choke valve controls the airflow when the engine is cold. As a result, the mixture gets richer as the throttle valve is expanded because more fuel is drawn from the main jet while less air is accessible.
A cold chainsaw requires a large amount of fuel to start. The choke plate shields the venturi, resulting in a very rich fuel mixture that aids in operating the engine. After starting the engine, you can remove the choke plate for normal operation.
Screws and Jets
The primary fuel jets and idle jets make up the fuel jets. The idle jets, usually three in number, stay open. When the throttle valve is held open, the venturi’s pressure falls to a level where the main jet can transport fuel. These jets have screws at their starting locations regulating fuel passage.
The H screw is used on the primary jet, while the L screw is used on the idle jets. A screw known as an idle screw is also present on the throttle. When the engine is idle, this screw regulates the valve’s location.
Related: Why Were Chainsaws Invented?
Understanding 2-Stroke Chainsaw Carburetors: How They Differ from 4-Stroke Carburetors?
2-stroke chainsaw carburetors differ from 4-stroke carburetors in several ways due to the different designs of the two types of engines.
Fuel Mixture
In a 2-stroke engine, the carburetor combines fuel and oil to lubricate the engine and burn for combustion. 4-stroke carburetors, on the other hand, only mix fuel and air because a separate oil system distributes oil.
Air Flow
Compared to 4-stroke carburetors, 2-stroke carbs have a simpler design with fewer moving parts. The air flows through the carbs and into the engine in a single direction, whereas the air intake and exhaust are separated in 4-stroke carburetors.
Fuel Delivery
The fuel delivery system in 2-stroke carburetors differs from that in 4-stroke carburetors. The fuel mixture is delivered to the engine via a small hole in the side of the cylinder wall known as the intake port in 2-stroke carburetors. This allows the fuel mixture to enter the engine’s crankcase, which is compressed and ignited. The fuel mixture is delivered into the combustion chamber via the intake valve in 4-stroke carburetors.
Adjustments
To maintain peak performance, 2-stroke carburetors must be adjusted regularly. The carburetor may need to be adjusted depending on the altitude, temperature, and humidity of the engine’s environment. Due to their more advanced design, 4-stroke carburetors require fewer adjustments.
You should understand these differences properly to ensure your saw runs smoothly and efficiently.
Chainsaw Carburetor Adjustment: Tuning Your Carburetor for Optimal Performance
Carburetor adjustment is an important maintenance task that will keep your chainsaw running smoothly and efficiently. Here’s a step-by-step guide to getting started:
Clean the Clogged Air Filter
Have you noticed that you’re using more fuel than usual, despite your working habits not changing? The prime perpetrator is probably your clogged air filter. To fix it, take off the cylinder cap. Take the air filter off.
Examine the air filter thoroughly to check for any breakage or dirt buds.
If there is a lot of grime, wash the filter in warm, soapy water with a soft brush before rinsing it until the water is clear. Reassemble the air filter on the chainsaw after letting it dry fully.
You can also have a look at the detailed guide on how to clean a chainsaw air filter on Chainsaw Guru!
Examine the muffler and the exhaust port.
The muffler and exhaust port are intended to control the passage of exhaust gasses and minimize noise, but over time, they may clog with debris and impair the engine’s performance.
The carburetor adjustment may be ineffective because of a blocked exhaust port or muffler, resulting in decreased power and increased gasoline usage. A clogged exhaust port or muffler can also cause the motor to overheat, which could seriously harm the chainsaw.
Before adjusting the carburetor, check the muffler and exhaust port to ensure they are clean and working correctly.
Set fuel adjustment settings
A good balance of power, fuel efficiency, and emissions are crucial. It’s important to adjust the fuel settings properly in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions.
Do make necessary adjustments on a regular basis to have a look at changes in temperature, altitude, and other elements that may have an impact on the engine’s performance.
Ensure the tank is more than half full.
When the fuel level is low, or the tank is empty, adjusting the carburetor can result in a too-rich carburetor emission when the tank is filled.
Warm up the engine
Turn it on and allow it to warm up. Allow the saw to run for a few minutes if it idles. When warming up the engine, never let the throttle go all the way open.
Set the idle speed
The recommended idle speed for a chainsaw will vary depending on the model and the company. However, as a general rule of thumb, many chainsaws start out well with a resting speed of about 2700 RPM.
If you don’t have a tachometer, you should change the speed so that the saw idles as high as it can without engaging the clutch.
Furthermore, it’s crucial never to set the idle speed so that the chain moves when you let go of the accelerator because doing so is risky and could lead to excessive chain and bar wear.
Set the low-speed fuel adjustment.
The chainsaw carburetor’s low-speed fuel adjustment regulates how much fuel is delivered to the motor at low speeds. A setting that is too rich can result in excessive smoke and poor throttle response, while a setting that is too lean can cause the engine to stall or operate badly at idle or low speeds.
The chainsaw can operate smoothly and effectively at low speeds, guaranteeing safe and optimal performance.
Each time a small change is made, the chainsaw’s functionality should be tested.
After finishing this step, your gas chainsaw will be correctly adjusted to run at an ideal speed without lag.
Read the detailed Carburetor Adjustment Guide Here!
Chainsaw Carburetor Problems: Common Issues and How to Troubleshoot Them FAQs
What is the work of a carburetor in a chainsaw?
A chainsaw’s carburetor controls the air-fuel mixture that drives the engine. It properly mixes fuel and oxygen before delivering it to the engine to produce combustion, which powers the chainsaw.
How does the fuel get to the carburetor in a chainsaw?
Fuel enters a chainsaw through the fuel line, which is attached to the fuel canister, and travels to the carburetor. Fuel is drawn from the tank via the fuel line and into the carburetor’s float bowl as the engine operates.
How does a 2-stroke carb work?
When fuel and air are combined in a 2-stroke carburetor, the mixture enters the carburetor through the air filter and moves through the venturi tube, which produces a low-pressure area that draws fuel into the air stream. After mixing with the air, the gasoline enters the engine’s intake manifold.
What are the three functions of a carburetor?
A carburetor’s three primary jobs are to control the air-fuel ratio, deliver the right quantity of fuel for the engine’s demands, and manage idle speed.
What controls fuel flow in a carburetor?
The main and idle jet in a carburetor regulates the gasoline flow. At fast speeds, the main jet regulates fuel flow; at low speeds, the idle jet does the same.
What increases fuel in the carburetor?
Adjusting the primary jet or the needle valve, a carburetor’s fuel capacity. This regulates how much fuel is supplied to the engine and blended with air.
What controls the fuel level in the carburetor?
The float bowl and the float regulate the fuel amount in a carburetor. When the fuel level in the bowl hits a certain level, the float rises and closes the needle valve to stop more fuel from entering the bowl.
Conclusion: How Does a Chainsaw Carburetor Work?
In summation, the chainsaw carburetor is an important part of any chainsaw, and regular maintenance is necessary for it to operate at its best and last the longest. Your chainsaw will operate more smoothly and effectively if the carburetor gets regular cleaning and adjustment. This way, you lower the likelihood of malfunctions and expensive repairs.
Always read the user manual for your chainsaw for detailed instructions and safety precautions. Also, always wear the proper protective gear when using your chainsaw.
Chainsaw engine can give you many years of dependable service with the right upkeep, enabling you to take on even the most challenging cutting tasks easily.
- Stihl GTA 26 Garden Pruner Mini Chainsaw Review - September 16, 2023
- Stihl MS260 vs 261 – [Battle of Power and Reliability] - August 16, 2023
- Husqvarna 120 Mark II vs Stihl MS 170 – [Detailed Comparison] - August 1, 2023
